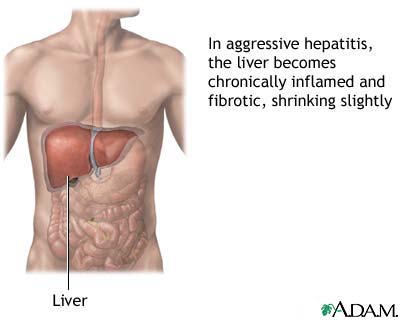
Hepatitis B is the inflammation, swelling and irritation of the liver because of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). a lot of people who have persistent hepatitis B encompass little to no signs and symptoms; as they may not even appear sick. as an effect, they might not discern they are infected. on the other hand, they can still multiply the virus can spread to other people.Symptoms may not emerge for up to six months following the point of infection. Early symptoms may consist of loss of appetite, fatigue, low-grade fever, joint and muscle aches, nausea and vomiting, yellow skin and dark urine because of jaundice. People having chronic hepatitis may show no symptoms, although continuing liver damage may take place. They may acquire some or all of the signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis.the HBV spreads and be transmitted via blood, vaginal fluids, semen, and other body fluids. Infection can happen if you have undergone blood transfusions, blood contact in health care settings, had direct contact with the blood of an infected person by touching an open wound or being pricked with a needle, had unguarded sex with an infected person, received a tattoo or acupuncture with contaminated devices, shared needles during drug use, and shared personal items like toothbrushes, nail clippers, and razors with an infected person. Hepatitis B virus can be transmitted to an infant during childbirth if the mother also has the virus. Additional risk factors for hepatitis B infection includes being born or having parents who were born in areas with high infection rates like in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean; having manifold sex partners; men engaging in sex with other men; undergoing hemodialysis; and when infected with HIV.Hepatitis B infection may either be acute or chronic. Acute hepatitis B is a three to six month period after being infected. on the other hand, chronic hepatitis B is when the hepatitis B virus relics in a person’s body for so long. These people are recognized to be the carriers of the hepatitis B virus, even though they do not present any symptoms. the majority of the damage from the hepatitis B is caused by the body’s reaction to the infection. If the body’s immune system perceives the infection, it gives out particular cells to battle it off. Nevertheless, these infection-fighting cells may lead to liver inflammation.There are tests that are made to spot and observe liver damage due to hepatitis B, such as liver function tests, albumin level, and prothrombin time. and there are tests done to help in diagnosing the infection like the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), in which the positive result indicates having active infection. Also, antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (Anti-HBc) in which positive result shows you had current infection or have a history of the infection. another is antibody to HBsAg (Anti-HBs) wherein positive result indicates you either have had hepatitis B before or have received hepatitis B vaccination. most of these hepatitis tests are available at various STD clinics and can be taken by anyone who thinks that they have the illness. This is the easiest and most accurate way to detect the disease.