my girlfriend and I have been dating for a few months now and recently i have symptoms of an std, we both have got checked out my results were positive and her's were negative how is that possible if I never cheated? Could I have carried the disease into the relationship and just not passed it?
WTF! maybe they didnt test her properly lol
It is very possible not to transmit to your partner, but every time you have intercourse, you are raising the possibility of transmission. First things first, never have unprotected sex again. Never. Gonorrhea is very serious, especially when a female contracts it because it can render her unable to have children. Also, if she were to become pregnant for any reason, gonorrhea has been shown to cause birth defects in babies. Men too can face sterility if the urethra becomes inflamed from the disease process. secondly, I would have her retested again in approximately 3 months. Until then, no unprotected sex, ever. 80% of women never have symptoms of gonorrhea, so it is important that she continues to be tested. what she needs to request from her OB/GYN in the way of testing is an ELISA, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. this test is FAR more sensitive than a regular culture or blood test and will detect even trace amounts of gonorrhea. IF your doctor has placed you on antibiotics, take them until you are finished with them. do not stop them even if your symptoms have decreased. That is the only way that they will be effective.
Hope this helped.
Gonorrhoea is a highly infectious disease acquired by sexual intercourse or other intimate sexual activities and is commonly known as 'the clap'. it is caused by a bacterium called Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Gonorrhoea is still a significant problem in the world. it can occur in the genitals, anus and throat of both men and women, depending on the type of sexual activity. Gonorrhoea usually has a incubation period of 2-7 days after contact and the symptoms vary significantly between men and women.
In women, there may be minimal or no symptoms with a mild attack. When symptoms occur, they include a foul smelling discharge from the vagina; pain on passing urine; pain in the lower abdomen; passing urine frequently; tender glands in the groin; and fever. Whether symptoms are present or not, the infection can move further into the body, and involve the womb and fallopian tubes. this can lead to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease or inflamed ovaries.
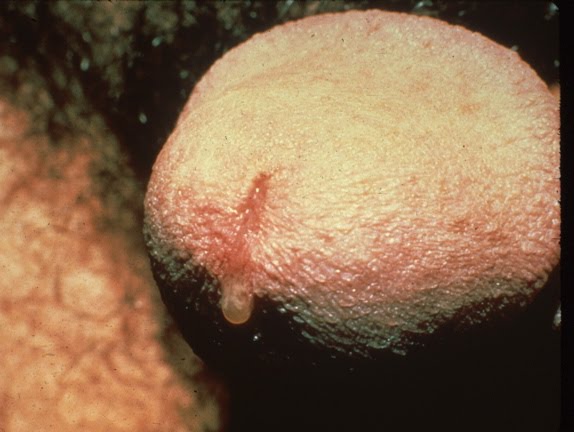
In men, the symptoms are usually obvious, with a yellow milky discharge from the penis, pain on passing urine and, in advanced cases, inflamed glands in the groin. If left untreated, the prostate can become infected, which can cause scarring of the urine tube, permanent difficulty in passing urine and reduced fertility.
If infection has occurred via the anus, an anal discharge, mild diarrhoea, rectal discomfort and pain on passing faeces are the common symptoms. Oral sex can lead to the development of a gonococcal throat infection.
Some other less common complications of Gonorrhoea include Gonococcal conjunctivitis; septicaemia; scarring of the uterus and fallopian tubes in women; and Gonococcal arthritis.
so if you had it you would have showed signs in 2-7 days after being exposed..