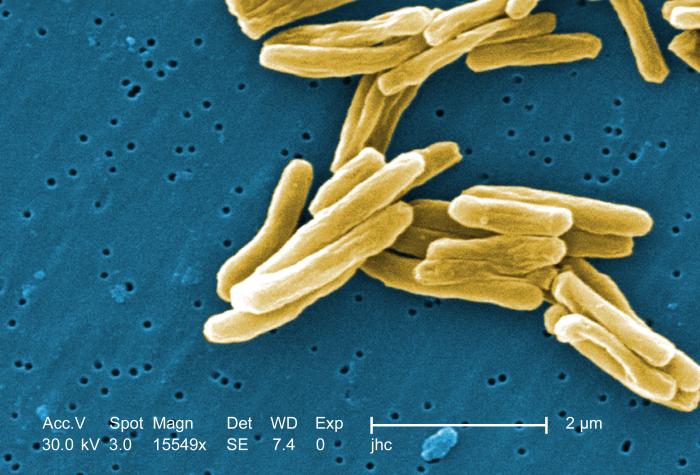
Disease: Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by germs transmitted through the air. It typically affects the lungs, but can also affect the brain, kidneys or spine. if left untreated, TB can be deadly.Symptoms: TB disease can cause feelings of sickness or weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats. TB disease of the lungs can cause coughing, chest pain and coughing up blood.Transmission: TB germs are transmitted when a person with TB disease coughs, sneezes, speaks or sings and another unaffected person breathes in the germs, which can stay airborne for several hours. that person contracts TB infection.TB infection versus TB disease: someone with TB infection has TB germs, but because the germs are inactive, the person is not affected or contagious. however, the germs may become active. someone with TB disease has active TB germs, which multiply and destroy body tissue. the person usually shows symptoms and is contagious.Testing: Those who have spent time around someone with TB disease should be tested for TB infection. Both skin tests and bloods tests are available. if one tests positive for TB infection, the person must undergo another test, generally a chest X-ray or sputum sample, to determine if they have TB disease.Treatment: Doctors usually prescribe drugs to people with TB infection to kill the germs and prevent TB disease. to treat TB disease, one must take several drugs for six-12 months.Prevention: a vaccine, Bacille Calmette-Guèrin, exists, but is generally not recommended in the United States. It does not completely prevent people from contracting TB disease and may cause a false positive skin test.Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Return to Paging Mode