Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus of mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not primarily attack the liver; the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect.
When doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they usually are referring to hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver. There are several hepatitis viruses; they have been named types a, B, C, D, E, F (not confirmed), and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types a, B, and C.
Difference between the different Hepatitis Symptoms
HAV — Hepatitis a Symptoms
Hepatitis a commonly occurs due to overcrowding of space and poor sanitation system. it is also known as Infectious Hepatitis as its transmission to the infected people id through food and water contaminated with fecal matter, hepatitis virus in the blood and on the hands of the people. The parturition period of the virus lasts between 15 to 45 days and the onset of the hepatitis can be very abrupt.
The sudden onset of the hepatitis is marked by the high fever. The Hepatitis B and C are different from Hepatitis a as in these two types the incubation period of the virus is much longer. The Hepatitis a virus infects over 150,000 Americans each year still the infection state never turns out to be chronic. Generally, all the cases are very mild without any complications.
HBV — Hepatitis B Symptoms
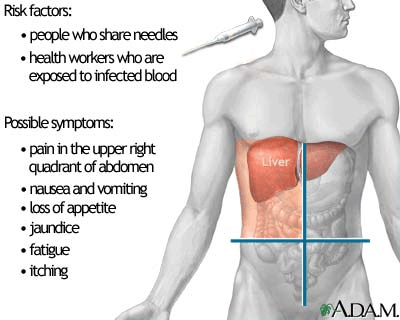
HBV is the common name for Hepatitis B virus in the medical circles. Other commonly referred names are Long Incubation Hepatitis and Serum Hepatitis. it is actually the most deterrent pathogen that happens to be bloodborne. More than 6800 health care professionals were infected by HBV in the year 1992. out of the 250 hospitalized, 100 died due to further complications in their infections. HBV has a rather long incubation period ranging between 50 days to 180 days during which the virus can potentially appear in the infected person’s urine, fecal matter, semen, sweat and tears; spreading across the body without any visible signs of it being there.
The beginning of HBV is often marked by mild flu-type symptoms coupled with Acute Hepatitis Symptoms. However, about 70% of the patients remain infectious for more than three months even after the acute stage symptoms have subsided. For 5%-10% of the cured patients, the case is altogether different, as they become lifelong carriers of the infection. Often these lifelong carriers develop liver cancer and cirrhosis. to keep the organ liver of these lifelong carriers in a healthy state, medical professionals prescribe chronic hepatitis patients for a milk thistle diet.
HCV — Hepatitis C Symptoms
You can pick HCV or Hepatitis C virus if you are exposed to contaminated blood. Occurring mostly in adults, it very common in Intra Venous drug users. it is a form of “Blood Transfusion Associated” Hepatitis. with an incubation period of 20 days to 90 days for the virus, most of the positive cases of HCV are unearthed between 5th and 10th week after exposure to virus. with the advancement of chronic stage, the infectious stage ends abruptly.
With an insidiously acute stage of HCV showing symptoms such as vomiting, jaundice, nausea and anorexia, more than half the HCV infected persons develop into chronic patients. Many even advance onto develop liver cancer and cirrhosis. Milk Thistle yet again is the most trusted diet by the healthcare professionals to keep their patient’s liver in a healthy state.
Find powerful herbal remedies Herbal Remedies for Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves relieving symptoms and maintaining adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Careful attention should be given to medications which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function. Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels.
In addition, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. it occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis B and hepatitis C usually involves medication or combinations of medications to eradicate the virus. Doctors believe that in properly selected patients, successful eradication of the viruses can stop progressive damage to the liver and prevent the development of cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Alcohol aggravates liver damage in chronic hepatitis, and can cause more rapid progression to cirrhosis. Therefore, patients with chronic hepatitis should stop drinking alcohol. Smoking cigarettes also can aggravate liver disease and should be stopped.
Fulminant hepatitis
Treatment of acute fulminant hepatitis should be done in centers that can perform liver transplantation since acute fulminant hepatitis has a high mortality without liver transplantation.