2010 ? 07 ? 05 ?
Chapter VIII of the pediatric TB
TB (Tuberculosis) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a chronic infectious disease, can affect various body control pipe to TB is most common. Onset of tuberculosis in children is more common in the original. Improper treatment. Prone to blood spread, causing miliary tuberculosis and tuberculous meningitis, the two diseases, TB is the leading cause of death in children. With the development of productive forces and universal BCG vaccination, anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy continue to improve, the incidence of this disease mortality rates decreased significantly.
urban and rural areas, the incidence of TB is very uneven, at present, remains a serious health hazard in children’s diseases. Clinical type of TB in children, showing so many more adults are different, the prevention and treatment of TB in children is an important national component of prevention, therefore, to understand some characteristics of TB in children, is essential for the prevention of tuberculosis.
Section characteristics of tuberculosis in children
I. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in children
(a) the incidence of infection with the human type Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children , bovine-based. Because children with immune dysfunction, susceptibility to tuberculosis in children were mainly focus on, but the infection does not mean disease. TB infection rate among means in the population currently infected with TB but not yet the percentage of the patients, generally through the OT or PPD test was positive crowd response to the detection rate of infection. Infection rate increased gradually with age.
(b) only when the body’s immune system to reduce, or intrusion into the quantity of bacteria, poison and strong only when the occurrence of tuberculosis. the prevalence of TB infection means the population has TB disease after the percentage of those.
in 2 to 3 years of age in children, not those kinds of BCG infection, which is equal to its prevalence.
(b) the infection source and transmission source of infection of TB in children, mainly for adult patients with tuberculosis bacteria row. TB patients with different adult, pediatric tuberculosis can often find a clear source of infection, such as family members, childcare workers or teachers in a row tuberculosis bacteria. La bacteria in close contacts of those children row. the prevalence and incidence rates than non-exposed children was significantly higher.
TB in children, mainly through the respiratory tract. TB patients cough, tuberculosis scattered in the air with the saliva, sputum or contaminated dry dusty floating in the air, when the susceptible children after inhaling the polluted air, under certain conditions, Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the lung the infection. Secondly, children of tuberculosis can be due to contaminated drinking unpasteurised milk, or sucking fingers contaminated Mycobacterium tuberculosis, spread through the digestive tract. Others, such as through the placenta, skin and mucous membranes communicators are rare, but transmission through the placenta caused by congenital TB should be attention.
Second, the clinical features of tuberculosis in children
type of tuberculosis in children by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children, can affect ?????. However, tuberculosis is still the most common.
1, children with pulmonary tuberculosis on the often divided into the following five types:
I type the original hair tuberculosis, including the primary syndrome and hilar lymph node TB (tuberculosis of bronchial lymph nodes) , more common in children period.
? type that hematogenous disseminated tuberculosis, including acute hematogenous disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis (acute miliary tuberculosis) and sub-acute and chronic hematogenous disseminated tuberculosis. Pediatric period, mostly for acute disseminated, and its severe illness and high mortality.
? type of tuberculosis that is invasive, including invasive and cheese subclavian pneumonia. Adolescence were more common.
? type of fiber that chronic cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis, which is the main source of infection of tuberculosis, in children with rare period.
? type that tuberculous pleurisy and pleural effusion.
2. Pulmonary tuberculosis pulmonary tuberculosis in children to the health of tuberculous meningitis in children most at risk, is the leading cause of death of tuberculosis in children.
other, such as bone and joint tuberculosis, urinary tuberculosis, abdominal tuberculosis, may occur in the pediatric period.
(b) the clinical features of tuberculosis in children.
1. the original hair Mycobacterium tuberculosis invades the human body occurred after the initial primary infection. Including the primary syndrome and bronchial lymph node tuberculosis, the main types of tuberculosis in children.
invasive pulmonary tuberculosis by the respiratory tract, the stay in the lung at the edge close to the pleura, the formation of the primary lesion, most of the primary lesion is only one, occasionally may have two or more, most of its parts the lower part of the right upper lobe. Primary infection, the body of the bacteria have not been allergic to state, therefore, lesions are often small. Part of the original lesion bacterial infection through the lymphatic nodes, the formation of lymphangitis, lymphadenitis. Primary lesions, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, collectively known as the three primary syndrome. Primary lesion and lymphangitis can naturally absorb more than recovered, but the cheese inside the lymph node lesions, long-term difficult to absorb, the formation of bronchial lymph node tuberculosis.
the clinical features of tuberculosis in the original hair is:
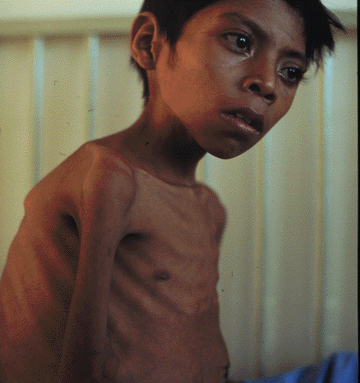
(1) the majority of children with no obvious symptoms; some children often slow onset, long-term low-grade fever, malaise and fatigue, night sweats, loss of appetite loss, weight gain, or even gradual weight loss and other TB symptoms.
(2) respiratory symptoms often not obvious, some patients may have cough, sputum, lung examination no positive signs, the body can be mild or moderate enlargement of lymph nodes; enlarged lymph nodes bronchial compression , may appear similar to whooping cough, spasmodic cough, asthma or breathing difficulties and other symptoms; recurrent laryngeal nerve compression, may appear a hoarse voice. Highly allergic condition in children, there may be erythema nodosum, or herpes simplex corneal conjunctivitis, joint pain and so on.
(3) Some children, expressed as easily repeated colds, bronchitis.
2. Acute miliary tuberculosis, acute miliary tuberculosis, tuberculosis of the former hair (primary syndrome or bronchial lymph node tuberculosis) caseous lesions rupture, the short term, a large number of TB spread by the blood of result is generalized miliary tuberculosis of the lungs performance.
the incidence of bacteremia than tuberculosis, the highly allergic condition in children is an important factor. more common in infants and young children infected in early tuberculosis 6 months, especially within 3 months, acute infectious diseases (such as measles, whooping cough, etc.) based upon disease and malnutrition are often an important incentive.
acute miliary tuberculosis clinical features:
most patients with acute onset of sudden high fever, severe symptoms of poisoning, pale, loss of appetite; can still have a cough, breathing breath, cyanosis and other symptoms, there were a few slow onset, manifested as fever, tuberculosis, symptoms of poisoning, often in the acute infectious diseases, the show weakness, night sweats, fatigue, chronic cough and other symptoms.
physical examination positive signs are often rare, about half of the children had superficial lymph nodes and hepatosplenomegaly, a small number of children with visible skin whitehead, nodules visible on fundus examination choroidal nodules, more common in the retina centers around the arterial branches. Pulmonary signs and more obvious, the course late, or could be heard and fine wet rales.
3. Clinical characteristics of infant tuberculosis
immunocompromised infants and children because the body is highly allergic state, is prone to bacteremia after TB infection, the primary lesion can occur liquefaction collapse. the further spread of the formation of specific clinical manifestations. a sudden high fever, body temperature 38 ~ 40 ?, for 2 to 3 weeks, after reduced to low heat, usually heavy. Symptoms associated with tuberculosis, severe cough, shortness of breath, hepatosplenomegaly, pulmonary symptoms, but less. There may be erythema nodosum and foam keratoconjunctivitis. If found to have clinical activity in patients with history of exposure to tuberculosis in infants, with pneumonia symptoms, longer duration, involving multiple organs, rapid development, the general anti-infection treatment when its effect is not ideal, should be considered in this disease. If the delay in diagnosis, the prognosis is poor.
4. Early TB infection
who have not traveled BCG vaccination and OT test-positive, or BCG and were strongly positive species (OT diameter ? 15mm) reaction, the body can not find the TB Early lesions are known as TB infection. may have a range of systemic symptoms, such as irritability, crying, or malaise, sleepily, anxiety, loss of appetite, weakness and easy fatigue, fever, headache, joint pain and other symptoms, and some may have no symptoms; others showed only recurrent respiratory tract infections. Examination, can be found in superficial lymph nodes and spleen slightly enlarged, bubble corneal conjunctivitis, erythema nodosum and so on. Chest X-ray examination was normal, could not find other parts of tuberculosis. Antibody test positive for TB, the symptoms improved after TB treatment diagnosis.
outcome of tuberculosis in children tuberculosis in children is most common in the original hair, the general who was healthy after, such as early diagnosis, proper treatment, the machine off strong immune function, the incidence of 3 to 6 months after the lesion began to absorb or induration, may be absorbed in the 2 years healing and calcification. but when the body’s internal and external environment under adverse conditions, such as age is too small, malnutrition, reduced immunity, the disease may progress has been even worse.
three diagnostic characteristics of tuberculosis in children
early diagnosis is the prerequisite for cure in children as early as possible, while reducing the future chance to develop into adult tuberculosis should be taken seriously enough. in order to make the correct diagnosis of heart in time to be a detailed history taking, complete control of clinical symptoms and signs, the correct use of testing and X-ray data, a comprehensive analysis to make a reasonable conclusion.
(a) a detailed medical history to medical history, in addition to current medical history, the clear history of exposure to TB patients, quite helpful in the diagnosis of tuberculosis in children. TB child contacts, especially family members, and teaching staff in contact with children in the tuberculosis patients, the TB infection rate, incidence and prevalence rates than non-exposed children was significantly higher. Also note whether the acute infectious disease history prior to the onset, in particular, measles, whooping cough, tuberculosis in children is often an important predisposing factor. Performance with previous tuberculosis, such as erythema nodosum allergies, bubble corneal conjunctivitis, tuberculin skin test reaction enhancement. Can be used as diagnostic reference.
(b) asked whether the symptoms of TB should pay attention to the slow onset and long-term symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, weight gain or significant weight loss, fatigue, weakness, sweating, respiratory symptoms and more obvious, such as cough, hemoptysis, or dyspnea, and more of the show has been seriously ill. If the performance of the recurrent respiratory tract infection, should be alert to the possibility of TB infection. Some children may be no such symptoms, a sudden high fever in children, body temperature of 39 ? or so, 1 to 2 weeks after the delayed healing were reduced to low heat.
(c) signs of TB in children can often be found in superficial lymph nodes, to both sides of the neck lymph nodes is more common.
highly allergic condition in children, there may be corneal conjunctivitis or skin foam section erythema nodosum.
general cases, often no obvious signs of lung, often out of proportion with the extent of hilar lesions.
larger scope of the original lesion, there may be signs of lung charge for the dullness, such as percussion, tubular breath sounds or breath sounds reduced.
oppression of bronchial lymph nodes, a large number of caseous pneumonia, even could be heard and dry and wet rales.
related pleural disease may have a corresponding performance, such as the weakening of activity in the chest, percussion dullness,
large effusion can cause mediastinal shift, tachycardia, decreased breath sounds and so on.
TB in children, may have small to moderate hepatosplenomegaly.
(d) X-ray chest X-ray examination is an effective method for early detection of TB, anteroposterior plain film, if necessary, into line with the lateral radiograph and CT, the lesions can be detected the type, scope and focus activities, and compared with non-tuberculous disease identification, regular review to understand the treatment of TB diagnosis, treatment has some significance.
(e) the current tuberculin test, tuberculin test of clinical application of antigen, there are two, namely the old tuberculin () and M. tuberculosis purified protein derivative (), where by TB tuberculosis infection (including BCG) after 4 to 8 weeks, for the tuberculin test the significance of the diagnosis of tuberculosis are subject to certain effects, but careful observation, attention to natural infection and artificial infection of positive identification, the methods of tuberculosis diagnosis of children still important means of existing.
1, naturally infected with human infection (BCG vaccination) after the identification of OT test responses (Table 8-1). Table 8-1 after BCG vaccination in naturally infected tuberculin test for a differential response (Table 8-1)
naturally infected with BCG vaccination
flush reaction induration diameter ? 15 mostly mostly 10mm ± a ? 15
flush sclerosis longer duration, 7 to 10 days fade, and the remaining 3 to 4 days pigmentation faded, difficult pigmentation
features flush induration hard, dark red, blush can be a double circle, clear edge, can be blistering, desquamation soft, light red, the edge is not clear, dry light or scaling
duration of short-term positive no less inclined, or even permanently weakened the positive negative 3 to 4 years.
2, OT test responses and clinical significance of the results of the record
the domestic practice of using OT as intradermal injection, 1:1000 concentration usually first to start the side of the forearm in subjects 1 / 3 at the junction of intradermal injection of 0.1ml (equivalent to tuberculin 10u), after 48-72 hours of observation, according to the diameter of induration at the injection site flush to determine the intensity of positive reaction; if no response, may then take a : 100 dilution of 0.1ml repeated tests, still no response to the basic TB infection can be ruled out; for highly suspected tuberculosis who wish to start from the 1:10000 dilution, and then in ascending order of concentration. Recently, the domestic application of PPD gradually replace the OT (0.00002mgPPD ? 1 tuberculin units). OT test reaction results criteria of Table 8-2. its clinical significance is:
test criteria of Table 8-2 OT
reaction results recorded local reactions red hard-diameter symbol (mm )
negative ? no red, hard -
suspicious ± flush sclerosis 20
(1) that have received positive tuberculosis infection, including human infection (BCG vaccination ) and natural infection. BCG vaccination can be found in 4 to 8 weeks, or activity by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection but no lesions, or TB, or who have had TB lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical cure but not all dead.
? species of BCG is not the emergence of positive reaction of 3 years of age, especially in children under 1 year of age, suggesting recent infection, the body to have active lesions, age of the smaller, more likelihood of active TB large. If the Department of asymptomatic children, but only OT was generally positive, suggesting that old infection, and more without active lesions.
? OT test showed strong positive reaction, whether or not vaccinated with BCG, the body may have active lesions, other relevant checks should be carried out, early diagnosis.
? two years, OT test from negative to positive or weakly positive to strong positive reaction, the reaction diameter increased ? 6mm, suggestive of recent infection, and there exists the possibility of active lesions.
(2) negative for tuberculosis infection that is not received, or BCG vaccination was not successful. 1:100 OT test is still generally considered negative, can be other than tuberculosis. the following conditions may cause false negative:
? primary infection tuberculosis, but not for long (4 to 8 weeks), the body still produce specific allergy.
? cellular immune dysfunction, such as congenital immune deficiency or transient immune function (found in severe infection, acute infection, the application of immunosuppressive agents during middle), and false negative reactions:
To determine whether the low cellular immune function, which can test for PHA were observed, such as the OT test was negative reaction to PHA test were positive, then the prompt immune function properly, TB can be ruled out; such as OT test was negative and the PHA test also was negative or weak positive reaction, suggesting that immune function should be further for the inspection; when determining immune function, and clinical and X-ray results suggest a possible TB advised to promote the use of immune agents such as transfer factor therapy for some time, now repeat the OT test, if you will help to positive diagnosis.
? tuberculin test was failed or error.
(f) other laboratory tests
1, look for TB according to the disease, choose sputum, pleural effusion, ascites or cerebrospinal fluid samples to find TB, such as by the positive results, can be diagnosed tuberculosis. Since infants do not spit, and more will be swallowed into the stomach in sputum, gastric lavage with normal saline can be used. taken to check gastric washing, all samples positive rate of bacteriological examination, and skill levels with the disease have a certain relationship, put checks tuberculosis positive rate of sputum smear and thick direct method; also can be directly fluorescent antibody test for inspection. TB culture positive results, if any, can also be susceptibility testing to guide clinical treatment; occasionally subject to animal inoculation.
2, lymph node puncture smears and found that TB-specific changes, such as caseous necrosis, tuberculous nodules, can help diagnosis of nucleus, and can identify non-tuberculous lesions.
3, changing the blood of tuberculosis in children with disease-related changes in blood. the acute stage, total number of leukocytes and neutrophils were higher proportion of neutrophils, there may be a left shift and toxic particles; a small number of patients with severe, there may be leukocyte reduced or leukemoid reaction. Condition improves, the total number of normal white blood cells, eosinophils and lymphoid mononuclear cells increased the proportion. more red blood cells and hemoglobin in the normal range, or showed mild anemia changed.
4, ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate of increase or decrease, can be regarded as an index of improvement condition, gradually recovered after treatment ESR can be proved to have active disease previously. but the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, can not completely rule out active disease.
5, detection of tuberculosis in children with immune cell targets immune function, manifested as lymphocyte transformation rate is lower than normal; humoral immunity has actually strengthened, and gradually with the restoration of normal conditions, such as increased, mainly specific antibodies increased, while IgM was normal. 3H-TdR clinical parameters can be detected by lymphocyte transformation into, this method is more objective and sensitive than the conventional method, but also the actual working conditions, using different antigens such as PPD, aggregated OT, Ag5 or Ag6 so, the choice of ELISA method to detect patients levels of specific antibodies, the results for the diagnosis of tuberculosis or pulmonary tuberculosis in children, determine treatment, plants were higher practical value.
(g) of active TB in children and indications for determining the following for reference:
1, the sick child age, history of exposure to tuberculosis and OT test positive among the three Relationship: no species of BCG vaccine in infants under 3 years of age, history of close contact with TB, OT test positive, even if uncertain whether the X-ray signs of tuberculosis, the possibility of tuberculosis should be considered, and appropriate treatment should be periodically observed ; the case of infants under 1 year of age, suffering from active tuberculosis is the possibility of large, should be actively treated. OT test within two years from negative to positive, or weakly positive to strongly positive, the reaction time ? 6mm diameter to increase, suggesting new infections, many have active lesions.
2, body temperature observed active tuberculosis often irregular fever, but sometimes easily overlooked due to low heat. Timing is preferred method of temperature measurement, after a period of time to observe, to determine whether heat.
3, nutrition and weight infant tuberculosis, while not a major cause of childhood malnutrition, but the absence of other reasons, the course of time does not increase body weight, or even reduce, or malnutrition, should be careful to check whether active tuberculosis.
4, no other cause of elevated ESR, should be considered as active tuberculosis, the TB treatment gradually returning to normal ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate is further proof of active TB due to fast system.
5, find the TB sputum, X-ray suggestive of invasive disease, are indications for active tuberculosis in children.
four TB treatment in children
TB is a chronic infectious disease in children and requires a longer period of treatment can effectively control the pathogen growth and reproduction, until it is killed elimination of residual bacteria in the lesion, so that lesions have been restored, to achieve a lasting cure. therefore, in determining the principles and methods of treatment, first the type of tuberculosis should be clear, the current focus on progress, with or without activity. Secondly, we must pay attention to children’s general condition, especially liver and kidney function was, in the treatment process, a planned follow-up to observe whether the medication in a timely manner, any changes in symptoms, there are toxic side effects and so on, to try to avoid contact with measles , scarlet fever, whooping cough and other acute infectious diseases, to prevent transmission of tuberculosis aggravated the situation. TB in children should use the following comprehensive treatment of chemotherapy-based measures.
(a) general treatment of systemic therapy generally is the basis for comprehensive treatment. by systemic therapy, and fully mobilize the body’s resistance to diseases, can better play the role of antimicrobial chemotherapy, to achieve better therapeutic effect. General treatment of the body, including:
1, a reasonable supply of nutrients is mainly rich in protein, vitamins, especially vitamin a, D, C food.
2, room air circulation, fresh, light is better.
3, suitable for indoor and outdoor activities, except symptoms weight, severe cough, a high degree of failure are advised bed rest, in general, the disease can be appropriate in accordance with indoor and outdoor activities.
(b) of the 40 years since chemotherapy, the clinical application of anti-TB drugs and chemotherapy continue to develop and perfect the treatment of TB increased substantially. At present, isoniazid, streptomycin and ammonia acid is recognized as the drug of choice is called first-line drugs; other anti-TB drugs as second-line drugs, used first-line drug resistance on the case, or because of side effects and can not using the first-line drugs, or re-treated in children.
1, the theoretical basis of tuberculosis chemotherapy
antibacterial anti-TB drugs, TB depends on the metabolic state of the body, the drug concentration and penetration of two aspects.
TB among TB patients the metabolic status of the body, can be roughly divided into: ? breeding bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis that is in the breeding season, such as open holes in the bacteria and other lesions in this category. they split the active metabolism, anti-TB drugs for such bacteria most significant bactericidal effect. ? stubborn persistence of bacteria and fungi that are in the resting phase of TB, such as the closure of TB lesions and macrophages in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other occasional division, which split the stagnation, slow metabolism, anti-TB drugs for such bacteria effect was weak, nor can it kill or sterilization, can only rely on slow and clear them of immunity.
lesions concentration of anti-TB drugs to reach the minimum inhibitory concentration in vitro (MIC) of 10 times or more, can play a bactericidal effect; as 10 times, you can only play antibacterial effect. Difficulties of this, increase the peak blood concentration, and efficacy are closely related. Of conventional doses of anti-TB drugs, the use of Dayton Directions to raise the peak in the blood, can improve drug efficacy and unlikely to increase toxicity. another factor affecting drug efficacy, is the penetration of drugs. Isoniazid, rifampicin has strong penetration outside the cell, can reach more than 10 times the MIC, both inside and outside the cell can kill M. tuberculosis, caseous lesions of the bacteria to kill a certain effect, called the full bactericidal drugs. Streptomycin in the cell outside the reach MIC10 times, and neutral to slightly alkaline extracellular environment, the role for streptavidin, while in the cells can not reach MIC10 times; ci amide hydrochloride in cells up to MIC10 times , and the acidic intracellular environment suitable for sterilization bared play amide hydrochloride, streptomycin, and ci are known as bactericidal drugs amide hydrochloride, and the remaining belong to antibacterial drugs.
2. the principles of chemotherapy reasonable treatment of TB in children, from TB in the body’s metabolic state and performance of both drugs be considered in the development of chemotherapy must be followed early treatment, adequate dose, drug laws enough treatment, combination therapy, sub-therapeutic principles: ?early, joint, adequate, regular, full?
(1) growth and reproduction of early treatment can rapidly destroy the active TB, in order to facilitate disease Early repair of tissue, can not stay for after-effects.
(2) sufficient to maximize the dose of anti-TB drugs in order to play the role of bactericidal or bacteriostatic, and children can also produce significant tolerance to the drug without the side effects, ensure the completion of full course of treatment.
(3) laws that have been suppressed before treatment or reduction of M. tuberculosis, no longer an active breeding opportunities, and prevent the generation of resistant bacteria.
(4) treatment can eliminate stubborn enough bacteria to prevent disease progression and recurrence.
(5) combination therapy to prevent TB drug resistance and, therefore, must choose a synergistic effect of the drugs in combination. on the same side effects, there is cross-resistance and the effect is too weak drug combination should be avoided.
(6) sub-treatment in two stages: ? intensive treatment phase and long-term chemotherapy is generally 6 months, short-course chemotherapy for 2 to 3 months. Application at this stage a strong anti-TB drugs in combination therapy to achieve rapid eradication of susceptible bacteria and the purpose of active growth and division. ? phase of consolidation therapy, chemotherapy, mostly long-range 12 to 18 months, short-course chemotherapy more than 6 months. Designed to eliminate stubborn bacteria. Consolidate the curative effect and prevent relapse.
3. Long-term application of standard chemotherapy with standard chemotherapy for tuberculosis, is isoniazid, streptomycin and other drug composition, various types of TB medication, dose and treatment in Table 8-3, with a course 12 to 24 months, because of course a long and difficult to adhere to the whole course of treatment, it is easy to relapse.
Table 8-3 species of various types of TB drugs, dosage and treatment
disease based dose regimen
(daily mg / kg) use of treatment ( May) Remarks
Results hormone test positive children
different in OT (1:2000 ) or PPD (5a) for the skin test induration diameter of ? 10mm.
associated with TB symptoms who were positive conversion within one year of open pulmonary tuberculosis patients and contacts.
measles vaccine measles, whooping cough, or flu using general anesthesia for surgery.
undergoing immunosuppressive treatment period.
original hair tuberculosis
6-12 EMB daily 20mg/kg ,6-8 weeks to reduce daily 10mg/kg
original hair tuberculosis (active type) and bronchial tuberculosis INH
SM intramuscular injection 1 month after switching to EMB. ? tuberculosis associated with bronchial obstruction can enhance pine daily 1mg/kg6 ~ 12 ?
acute Su tuberculosis
and tuberculous meningitis
INH daily maximum of 500mg (including intravenous and oral), severe illness, coma may be intravenous infusion. after 1-3 months in sufficient quantities. Discretion to reduce the daily 10mg/kg
RFP does not exceed the maximum daily 450mg
SM maximum of 750mg daily should be regularly measured by listening. after 4 weeks, replaced 3 times a week, sustained for three months.
severe cases, PAS can be dissolved in 10% of the full amount of glucose solution (diluted to 2-4% dark infusion), finished in 2-4 hours, drops should be freshly prepared.
disable the RFP should be the second program was added EMB.
recorded from the The rate of patients adhere to medication and treatment is inversely proportional to, therefore, shorten the course of treatment has attracted widespread attention and has achieved initial success. Two full bactericidal drugs, in particular stages of treatment is to strengthen the four drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin, streptomycin, pyrazinamide) was used, six months may be satisfied with the treatment regimen. Domestic short-course chemotherapy of tuberculosis in children is also explored in the program. Resistance in children considered poor, tubercular meningitis complicated by factors such as short-course chemotherapy of tuberculosis in children, due to nine months. such as the intensive treatment phase, the choice of isoniazid, rifampicin, streptomycin three drugs for three months, the first phase of consolidation therapy with isoniazid rifampin for three months, then isoniazid and then three months.
five, children of tuberculosis prevention
(a) increasing the body’s immune system
1. Inoculated with BCG by artificial means, will be attenuated bovine tuberculosis made vaccine strains, inoculated in the human body, the body immunity against TB. the effect is certain, but not absolute. BCG vaccination can greatly reduce the original hair tuberculosis and tuberculous meningitis incidence and mortality. in addition to a first vaccination at birth, but also in 5 to 7 years, respectively, 12 and 18 to 20 years for multiple cropping, each 8 to 12 weeks after inoculation for the OT to test, to check the vaccination effect, if negative should be re- replant. Generally speaking, intradermal inoculation method, OT test positive the higher rate of skin scarification the turn positive rate less than 50%. Positive tuberculin test, acute infectious disease recovery, the injection site include eczema, congenital thymic hypoplasia or child patients with severe immune deficiency, are not vaccinated against tuberculosis.
2. To strengthen nutrition and physical exercise to increase body resistance to the anti-positive children with acute infectious diseases.
(b) of the isolation source of infection
the original transmission of TB in children, primarily of adult patients with active tuberculosis, especially in close contacts such as family members and teaching staff in the smear positive patients . therefore, should actively find the source of infection, and provide isolation and treatment. To protect children from infection. Also, pay attention to environmental health, banned spitting, to strengthen the management and inspection of dairy cattle, dairy products be boiled disinfection.
(c) of the drug prevention
no species of BCG, OT test-positive infants and children under 3 years old, patients with sputum positive pulmonary tuberculosis in close contact (such as parents, family members or other teaching staff) in infants and young children, BCG has been planted and OT test showed strong responses (Results diameter ? 15mm), shall be a daily oral isoniazid 10mg/kg, preventive therapy, treatment for 6 to 12 months . OT test positive for children in the measles, whooping cough and other acute infectious diseases, should be a daily oral isoniazid 10mg/kg, the prevention and treatment, to the disease returned to normal immediately after discontinuation of treatment. To be used for other diseases, adrenal cortex hormone therapy, and OT test positive patients, taking hormones during the day should take isoniazid 10mg/kg, to prevent the spread of tuberculosis, recurrent.